Thanks to modern technology, the building materials market is expanding year by year. Creating complex translucent structures has become much easier thanks to a new polymer plastic - polycarbonate. It combines all the qualities necessary for this - strength, flexibility, low weight, translucency and aesthetics.
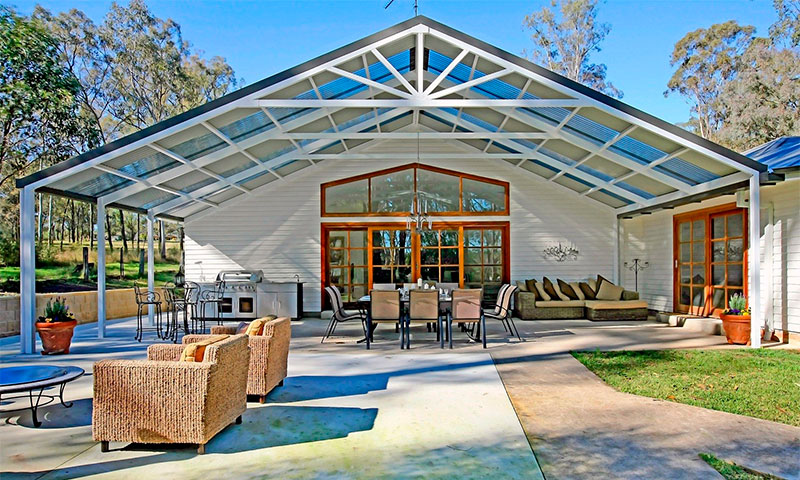 The popularity of polycarbonate is growing every day. Demand, as you know, creates supply, so the market is saturated with products from a large number of manufacturers. The proposed article will provide the information necessary for selection and make it easier.
The popularity of polycarbonate is growing every day. Demand, as you know, creates supply, so the market is saturated with products from a large number of manufacturers. The proposed article will provide the information necessary for selection and make it easier.
Content:
The best manufacturers of polycarbonate - which company to choose
World leaders in the manufacture of high-grade polycarbonate - European manufacturers:
1. Polygal plastics
2. Bayer (TM Makrolon)
3. Brett martin
4. Polyu italiana
The products of these enterprises meet international standards.
It is somewhat inferior to it, but polycarbonate of the best Russian manufacturers also differs in high quality:
1. Carboglass
2. SafPlast
3. Polyalt
Types of polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is divided into three types: monolithic (cast), profiled and cellular (cellular). Depending on the type of material and its technical characteristics (thickness and density of the sheet, the number of jumpers and their location in the honeycomb polycarbonate) plastic is used to perform certain works.
Monolithic polycarbonate
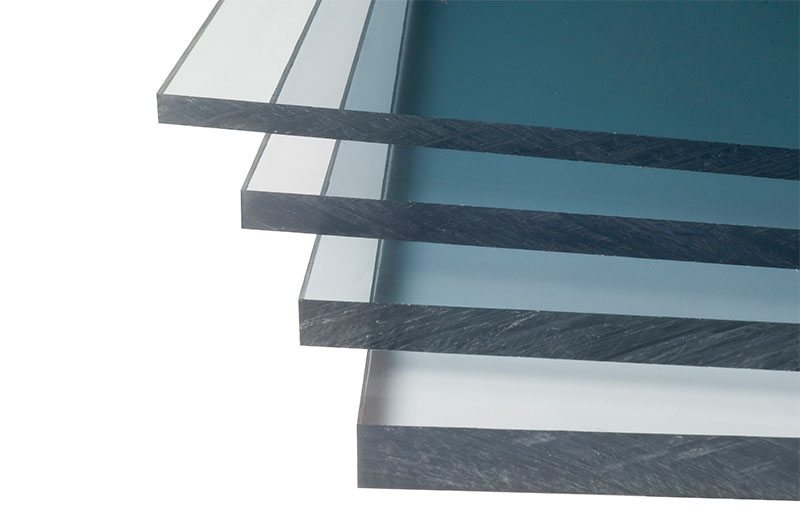

This is a solid polymer sheet with a thickness of 1 to 12 mm, devoid of internal voids and externally resembling acrylic glass (plexiglass). Some manufacturers produce panels with a thickness of up to 20 mm. Sheets can be colorless, transparent and translucent, colored, with a lower degree of light transmission.
The considerable density and viscosity of the polycarbonate obtained by the injection method increases its resistance to mechanical loads. The impact strength of the polymer is 1000 kJ / m².
The multiplicity of the excess of this indicator in comparison with other popular materials used in the construction of translucent structures:
- Plexiglas - 60;
- Polystyrene - 150;
- Silicate glass - 200.
Monolithic polycarbonate panels resist to bad weather, they are not afraid of hail, strong gusts of wind, and heavy snowfall. From very strong blows the surface can crack, but a multitude of dangerous sharp fragments, which can be injured, is not formed.
If necessary, the panel can be bent, giving them an arched shape. The bending radius depends on the thickness of the polycarbonate - the thinner the sheet, the smaller the radius.
Monolithic polycarbonate is frost resistant. In the absence of mechanical loads, the material withstands temperatures up to -50 ° C, and at -40 ° C, it also carries a shock load. The heat resistance of most brands is +120 ° C, and in some up to +150 ° C.
Not only translucent structures are made of polymer, but also shock-resistant and noise-proof screens used in interior design.
Benefits:
- High impact resistance;
- The ability to pass a large amount of sunlight (up to 90%);
- The small weight simplifying transportation and installation;
- Ease of processing: sheets are easily cut, sawn, drilled;
- Resistance to temperature changes;
- Excellent heat and sound insulation quality;
- The ability to block ultraviolet radiation due to a special protective layer;
- Moisture resistance;
- Fire resistance - the material melts, but does not burn;
- Safety in use;
- A variety of color shades, color stability.
Disadvantages:
- Instability to scratches (the world's leading manufacturers have mastered the production of monolithic polycarbonate with anti-abrasive coating, which protects the surface of the material from scratches and other damage);
- Technical solvents and acids leave streaks on the surface;
- A significant degree of thermal expansion that must be considered during installation of the coating;
- High price.
Profiled Polycarbonate
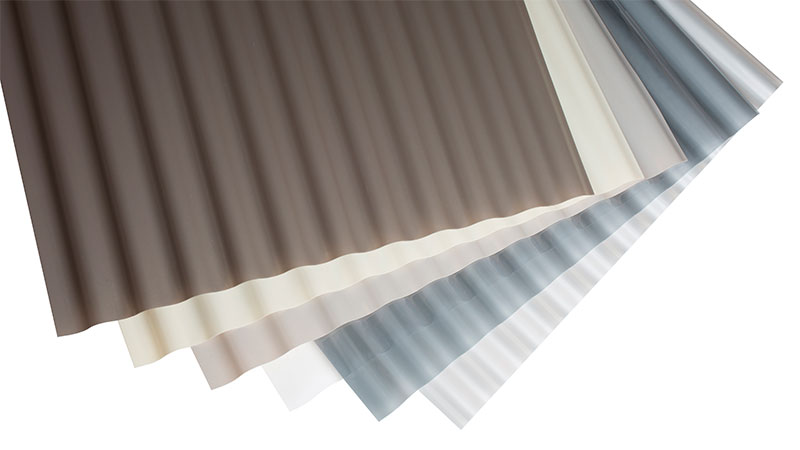

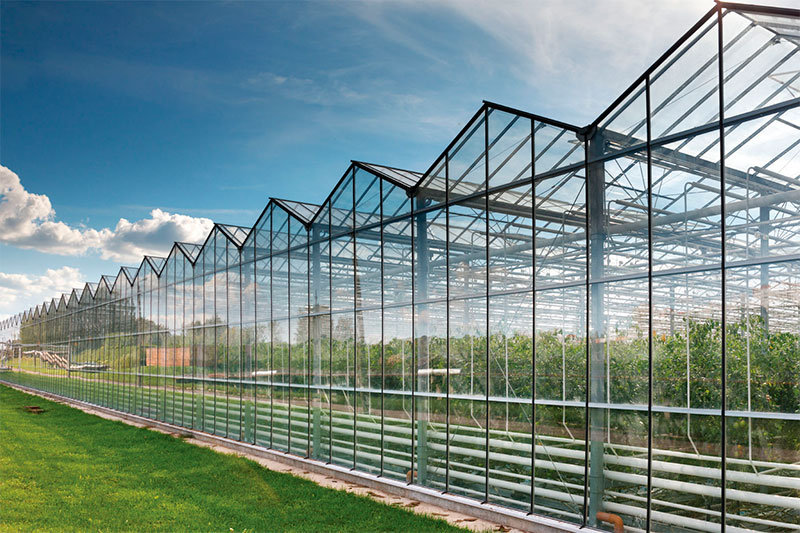
It is a constructional (bearing) material with the properties of translucent and decorative fencing. It is popular in private construction in the construction of greenhouses, fences, applicable as a roofing material. It can be attributed to a variety of molded polycarbonate.
Sheets with a wave-like or trapezoidal surface have a relatively small thickness (0.8-1.5 mm). Light translucent and transparent roofs of profiled polycarbonate are able to withstand loads of up to 320 kg per 1 m². As a roofing material, it can replace sheeting and ondulin.
Profile polycarbonate is divided by the size and shape of the wave, the degree of transparency and color. Transparent material may be colorless or color. Translucent panels, as a rule, are opaque or smoky, and opaque - bright.
Benefits:
- It has all the qualities of monolithic polycarbonate, and stiffening ribs repeatedly increase its reliability with a relatively small sheet thickness;
- The strength is comparable to the strength of metal sheeting, while the weight of the material is several times less;
- Resistance to corrosion;
- Light transmission up to 86%;
- Flexibility and ease of installation (can be used in arched structures);
- Resistance to fading;
- High sound insulation;
- Noiselessness (the sound of drops in the rain is not audible).
Disadvantages:
- Pretty high price;
- For fixing it is necessary to use special thermal washers, which guarantee reliable fixing of the sheet with temperature drops and changes in humidity.
Cellular Polycarbonate
The most popular type of polycarbonate used in the construction of greenhouses and greenhouses. The material has a more complex device than the previous types - several layers of plastic are connected by jumpers that provide rigidity. The voids formed at the same time increase the degree of noise and heat insulation of the material. Panel thickness from 4 to 50 mm.
Cellular polycarbonate is of several types:
- Single-chamber - 2 sheets connected by jumpers;
- Two-chamber - 3 sheets are connected by two rows of jumpers;
- Four-chamber - 5 sheets are connected by four rows of jumpers;
- Six-chamber - 7 sheets are connected by six rows of jumpers.
Stiffeners (lintels) can be located perpendicular to the sheet surface and at an angle of 45 °. The distance between the jumpers is also different: from 5.7 mm (in single-chamber polycarbonate) to 25 mm (in sheets that have more than two layers).
Some manufacturers produce cellular polycarbonate, the honeycombs of which are filled with airgel. It has increased impact resistance, and the degree of thermal insulation is such that it reduces heat loss better than three-chamber double-glazed windows with argon.
Benefits:
- Excellent thermal insulation properties;
- Uniform dispersion of light flux, which favorably affects the growth of plants;
- Frost resistance;
- Reasonable price for most plastics;
- Low weight relative to glass;
- Safety in operation;
- High impact strength.
Disadvantages:
- Large sailing (it is important to ensure reliable fastening of the panels during installation, otherwise strong gusts of wind will violate the integrity of the structure);
- During installation, you need to use special hardware, as the material has a significant degree of thermal expansion;
- Instability before abrasives and solvents;
- High price.
Polycarbonate Selection Parameters
Special attention should be paid to several basic characteristics of the material with regard to its further application.
Density
Its strength and ability to resist harmful environmental influences depend on the density of polycarbonate. It is important to consider that excessive compaction increases the weight and reduces the light transmission capacity of the material.
The average density of monolithic sheets is 1.18-1.2 g / cm³. Cellular panels have a density of from 0.52 to 0.82 g / cm ³, this changes the weight of the sheet, and its thickness remains the same. Various indicators of the density of cellular polycarbonate are caused not only by the thickness of the internal bridges, but also by their location.
Configuration of air channels and their corresponding density:
- Rectangular section - 0.52-0.61 g / cm³;
- Square section - 0.62-0.77 g / cm³;
- Hexagonal and triangular cross section - 0.78-0.82 g / cm³.
Weight
An important indicator of quality is the weight of 1 m² of plastic. The weight of the sheet, regardless of the type of polycarbonate, must correspond to the product of the density of the material and the area of the panel. Especially carefully, this indicator should be checked at the cellular polycarbonate, since the production of two sheets of the same thickness with a similar configuration of air channels can take a different amount of raw materials.
The lighter the plate, the lower its strength characteristics, as well as the snow and wind loads that it can withstand. Reducing the specific gravity of the plate reduces the price of the material, but at the same time decreases its quality.
In the entire history of polycarbonate production, a classic weight of 1 m² was formed for sheets of various thicknesses:
- 4 mm: cellular - 0.8 kg; monolithic - 4.8 kg;
- 6 mm: honeycomb - 1.3 kg; monolithic - 7.2 kg;
- 8 mm: mobile - 1.5 kg; monolithic - 9.6 kg;
- 10 mm: Cell - 1.7 kg; monolithic - 12 kg.
The weight of high-quality polycarbonate should be as close as possible to these indicators.
UV protection
From exposure to ultraviolet plastic quickly loses its elasticity and the ability to transmit light. After 2-3 years of being in outdoor conditions, the panel without a protective layer is destroyed.
Polycarbonate sheets, which are supposed to be included in structures in the open air, must be protected from the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays.
Manufacturers protect plastic in one of three ways:
1. Bulk protection - special additives are introduced into the granules of raw materials. This method is not effective enough, since the harmful radiation penetrates into the sheet. The service life of products is not more than 10 years.
2. Film protection or a thin layer of special coating (invisible) - reflects most of the rays. Service life - 15-18 years.
3. Volumetric filler in combination with a double layer of the UV barrier - the method ensures absolute protection of the material, the service life of 25-30 years.
Sheets, protected by the second and third method, have a special marking.
It is possible to draw conclusions about the degree of protection according to data on the package However, you can rely on the accuracy of what is written only if you have a certificate confirming the information.
Bend radius
When selecting a material for an arched greenhouse or for a structure with curved elements, the minimum bending radius for a particular type of polycarbonate should be considered. Depending on the type of material and thickness of the sheet, the bending radius ranges from 0.6 to 2.8 m.
During the installation of the panels do not neglect this data, since excessive bending will cause damage to the UV protective layer and the internal structure of the polymer. Subsequently, damage will reduce the life of the structure.
Color and light transmission
These are important characteristics of the material, since the degree of illumination and the temperature inside the greenhouse, under a canopy, depend on them. The amount of light that a polycarbonate sheet is able to miss depends on its color, degree of transparency, and thickness.
Indicative data for monolithic and cellular panels 4 mm thick:
- Transparent colorless - 90%, 74%;
- Yellow - 72%, 58.8%;
- Green - 36%, 27.9%;
- Turquoise - 36%, 21.3%;
- Blue - 34%, 23.3%;
- Red - 29%, 24%;
- Bronze dark - 25%, 17.1%.
What polycarbonate to choose

It is necessary to select the material taking into account the functional purpose and design features where the installation will be carried out.For all street buildings you need to purchase material with UV protection. For temporary outdoor structures erected for season 1-2, polycarbonate can be purchased without protection from ultraviolet radiation.
1. For the greenhouse
For the arrangement of greenhouses using transparent colorless polycarbonate honeycomb. Excessively thick sheets (with a thickness of more than 10 mm) absorb and scatter an excessively large amount of light (from 25 to 50%). This will adversely affect plant growth and reduce yields.
A thin panel will not help maintain the optimum temperature in the greenhouse. It is recommended to use material 4, 6, 8 mm thick. When choosing the thickness and density of the material, the climate zone is taken into account, where the greenhouse structure and the presence of a heating system will be erected.
2. For canopy
A functional and practical canopy without designer frills can be made of cellular panels with a thickness of 6-8 mm. To create a design that combines functionality and a spectacular appearance, you can use a monolithic or profiled polycarbonate. The flexible material is perfectly combined with wood, metal, including forging.
3. For fencing and roofing
From any kind of polycarbonate, you can build a fence. The use of translucent panels will create a special atmosphere of coziness on the site.
Popular use of profiled translucent sheets of bronze color in the construction of fences and roofs. The decoration of building elements with this material is in harmony with the landscape. For pitched roof pick up material with a wave height of not more than 15 mm.
How much is polycarbonate

The price of the material depends on the brand, type of polycarbonate, its thickness, sheet size, color, type of protection from UV rays:
1. Cheap products, as a rule, are made by manufacturers from low-grade raw materials, including secondary ones or using scrap and their own production.
2. Cellular polycarbonate of the “Light” or “lightweight” type is also distinguished by a lower price, but such material will serve only 2-4 years (the panel thickness of 3-3.5 mm is not designed for snow and wind loads experienced by Russian greenhouse buildings).
3. The price for high-quality cellular polycarbonate with a thickness of 4 mm is in the range of 200-280 rubles. for 1 m², 6 mm thick - from 350 to 450 rubles, 8 mm thick - from 430 to 550 rubles It should be noted that the material is sold in sheets with an area of 6.3 m², 12.6 m², and 25.2 m².
4. Price for 1 m² of domestic monolithic polycarbonate with a thickness of 1.5 to 3 mm - in the range from 530 to 1400 rubles., Thickness from 4 to 6 mm - in the range from 1450 to 2400 rubles., Thickness from 8 to 12 mm - in the range from 2850 to 4500 rubles. (with a leaf area of about 6.3 m²).
5. The price of profiled polycarbonate in the range from 500 to 1100 rubles. for 1 m².
It will be interesting to friends too







