The soldering iron in the home craftsman’s arsenal is as significant as the sewing needle for the zealous housewife. It will help to repair the failed electrical appliance, build up the cable. Someone he gathers dust in a box, extracted only occasionally, and someone uses it regularly.
Should I replace the soldering iron with a nichrome heater with a ceramic one, and a copper sting with a durable nickel-plated tip or an “old friend is better than the new two”? Recommendations for choosing an electric soldering iron for the home wizard.

Content:
The best manufacturers of electric soldering irons - which company to choose
The best tools are offered by manufacturers from Japan and Germany.
High quality, reliability, safety - products of the following brands meet all these requirements:
1. Hakko
2. Goot
3. Weller
4. Ersa
5. Matrix
The tools of these brands can be used by professionals and amateur electronics engineers, with its help you can even carry out the hard work of soldering SMD components.
Soldering iron design and principle of its work
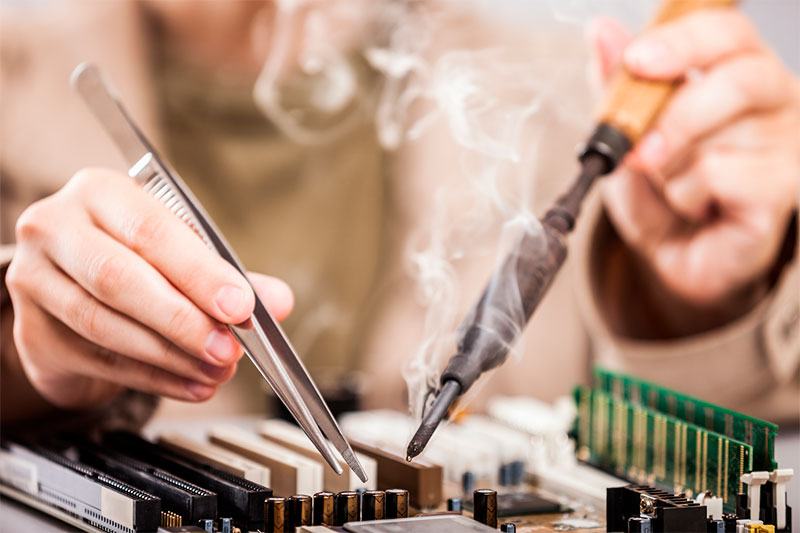

The main elements included in the design of a classic soldering iron:
- Sting (rod);
- Heater;
- Holder;
- Electrical cord with plug.
After turning on the soldering iron, the heating element is heated and transfers heat to the rod, which is made of a material with high thermal conductivity. A red-hot sting, the temperature of which can reach 450 ° C, melts the solder based on tin-lead, copper-zinc and other alloys. Solder fluid flows into the gaps of parts, and during cooling forms a solid one-piece connection.
Types of electric soldering irons
Soldering irons are divided by design and heating principle.
Nichrome soldering iron (EPSN)
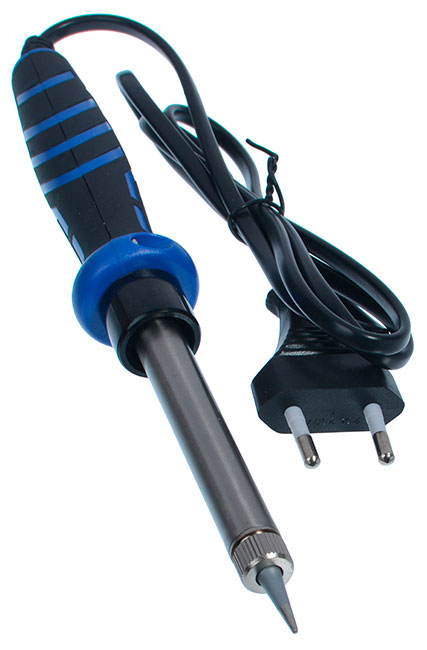

In an electric soldering iron with a spiral heater (EPSN) the heating element is made of thin nichrome wire (nichrome is an alloy based on nickel, which has heat-resistant properties).
In the simplest models, the turns of nichrome wire cover the body inside which the core is placed. For electrical insulation of the heater using mica tubes and plates, fiberglass cloth.
Benefits:
- Affordable price;
- Unpretentious in work, not afraid of mechanical damage and shocks;
- Maintainable.
Disadvantages:
- It takes a long time to warm up;
- Most models are not designed for intensive loads - with regular use (daily for several hours) it will not last long, as the coil burns out over time.
Ceramic Soldering Iron

This type of soldering iron uses a ceramic heater, which produces only a limited number of brands. Unfortunately, most of the tools on the market and positioned as a “ceramic soldering iron” are in reality a nichrome soldering iron with a ceramic insulator.
Pseudo-ceramic heaters are a ceramic rod with a thermocouple, which is covered by a nichrome spiral, the whole structure is covered with a ceramic tube. It can also be a ceramic tube with a nichrome thread inside.
The original heating element is a single tubular construction of a film heater, ceramics and thermistors. Such a heater is integral - thermistors and thermofilm are “imprinted” into ceramics.
How to determine the authenticity of the product? The butt of the “pseudo-ceramics” is rounded; inside the element there are four channels - two with nichrome winding, two with thermocouple wiring. On the lumen of the design is almost not translucent.
At the original element, a film heater is seen in the gap, passing through the thickness of ceramics in the form of straight paths, and a thermistor winding through snakes. The ceramic rod has a characteristic step at the end, and a narrow technological groove runs along the heater. These distinctive features are associated with the peculiarities of the technological process in the production of ceramic heaters. Although in pursuit of the opportunity to sell their products, unscrupulous manufacturers have learned how to forge both the step and the notch.
The main competitive trump card signaling a fake is low price.
Benefits:
- Fast heating;
- The fast-response control system maintains the set temperature even with an intensive heat sink from the tip;
- Considerable power at the small sizes;
- Long service life;
- It transfers heavy loads without burning out.
Disadvantages:
- High price;
- Most of the proposed tool with a "pseudo-ceramic" heater;
- The tool requires careful handling, and the fragile heating element can break from blows and falls. From accidental contact with cold liquid on heated ceramics, it may crack;
- The ability to use only "native" tips (it is desirable to choose a model with interchangeable nozzles).
Pulse soldering iron
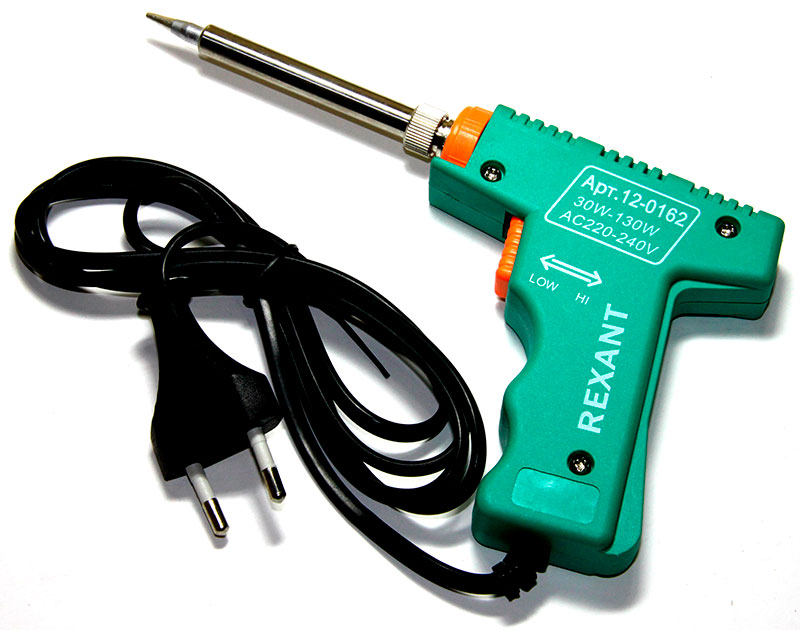

Unlike soldering irons of constant heating, the pulse is heated only by pressing the start button. Pulse models are designed for a short cycle of work and are in demand when soldering is only an insignificant part of the work process.
The design of the soldering iron includes a frequency converter, high-frequency transformer and microprocessor control circuit. The sting of copper wire, which is also a heating element, is attached to the current collectors of the secondary winding. The sting warms the passing current of low voltage. Recently, manufacturers offer pulse soldering irons, not only with a copper wire sting heater, but also with a ceramic heater and a removable tip.
The shape of a pulsed soldering iron resembles the letter “G”; such a shape is due to the need to press a button during the work process.
Benefits:
- Quick warm-up;
- Increased efficiency due to the operation of the heating element only at the time of soldering;
- The ability to solder both small and massive parts.
Disadvantages:
- Cannot be used during long work cycles.
Induction soldering iron
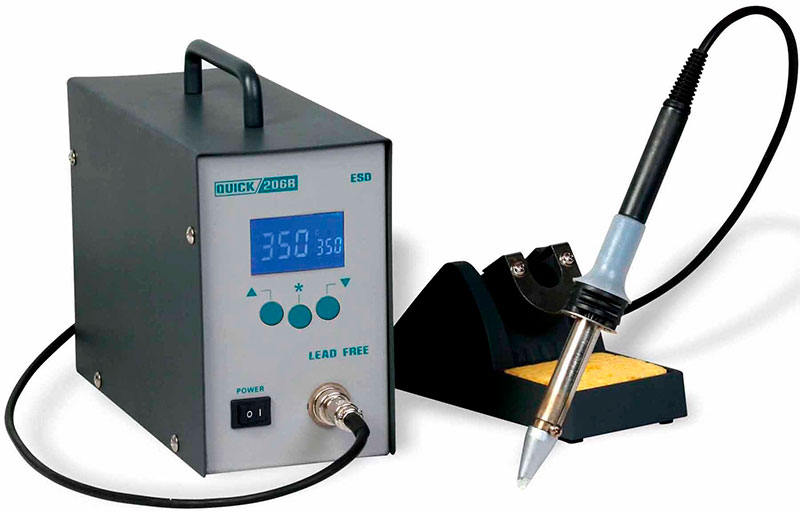

At the current time, an induction soldering iron is the pinnacle of technological advances in the field of metal soldering with low-melting solders. This type differs from traditional soldering irons by the heating principle.
A high-frequency magnetic field is applied to the working rod, which is generated by the induction coil. Inside the core there is a core with ferromagnetic properties, which heats up and then gives off heat to the sting.
Constant temperature conditions can be maintained in the traditional way (using a thermocouple or a thermistor that contacts the tip), or by replacing a nozzle with a ferromagnetic core that loses its ferromagnetic properties when a certain temperature is reached and stops supplying energy.
Benefits:
- Automatic maintenance of the heating temperature eliminates the need for the use of temperature sensors;
- Energy savings - not the entire volume of the tip is heated, but the surface layer;
- Uniform heating of the tip due to the absence of a heating electrode (the tip is a heater);
- Easy replacement of the working tip.
Disadvantages:
- High price;
- As a rule, it is an integral part of the soldering station;
- For each working temperature, a sting with an appropriate ferromagnetic core is required.
Cordless soldering irons
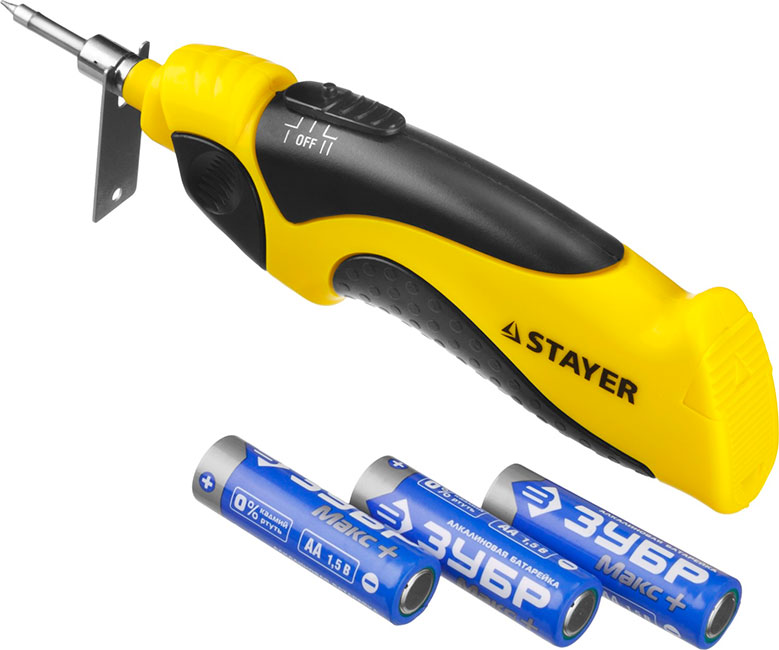

A low-power, battery-powered tool used in cases where it is not possible to work with a regular soldering iron: in the field, during a power outage.
Benefits:
- Fast heating;
- Independence from fixed mains.
Disadvantages:
- Little power.
Portable USB Soldering Irons
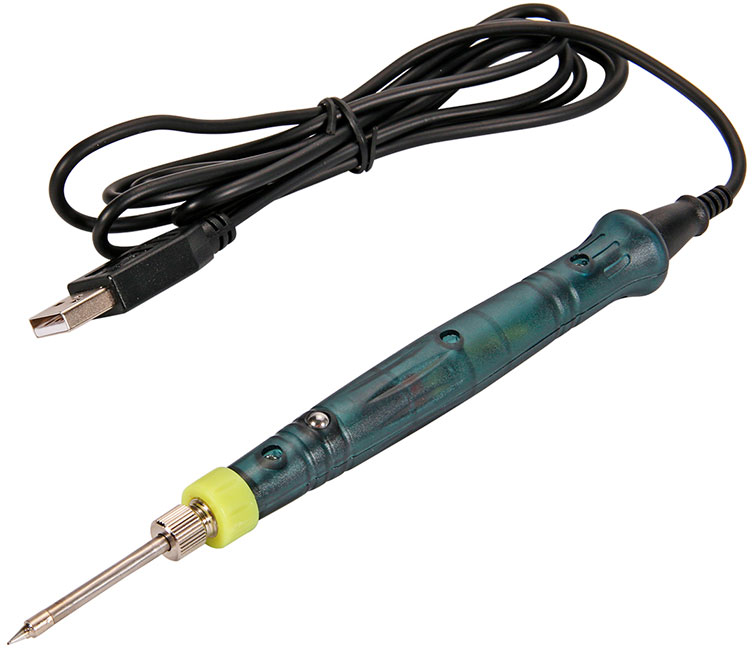

USB-powered mini-soldering irons can be used to solder small parts away from the outlet, you can connect the soldering iron to the cigarette lighter of the car using a special adapter.
Benefits:
- Compact and fast heating.
Disadvantages:
- Insignificant power.
Electric soldering options

Power
Select the power of the soldering iron should be based on the type of work in which you intend to use it. Soldering irons requiring high power are reliable and multifunctional. But their use in everyday life is inappropriate. Power universal household soldering iron, with which you can perform most of the work should be in the range of 25-40 watts.
If the power of the tool is insufficient, the soldering will take a long time or its quality will be unsatisfactory. Prolonged exposure to a weak soldering iron on contacts may cause them to overheat. A small temperature during operation can lead to “non-solders” that are not visually detectable.
Using a tool with a power much higher than necessary, it is possible to burn parts at the very first touch on them, which makes it difficult or impossible to further repair the appliance.
If you plan to solder contacts with a large area and weight, you need to increase the power of the tool, and not the temperature. The device with low power, but with a high temperature of heating can not cope with the dissipation of heat. Warming up of the overall tip used for propaying large parts depends on the power of the tool.
Temperature regulator
An error in choosing the temperature of the soldering iron during the repair of electrical appliances can result in the acquisition of expensive parts that can be damaged by overheating. The regulator can be built into the body of the soldering iron or be in a separate case.
The advantages of the instrument with a temperature controller:
- Ability to adjust the instrument to the desired melting point;
- When soldering circuit boards, the current-carrying paths will not detach from overheating;
- There is no need to change the soldering iron when performing work requiring different temperatures;
- The sting is not covered with scale from overheating.
Sting Material
The sting may be:
- Copper;
- Copper-coated (as coating used: nickel, aluminum, silver);
- Ceramic.
The copper sting is installed in ESSN-type soldering irons.
Advantages of a copper sting:
- Excellent thermal conductivity and heat capacity (when soldering a massive cable, the billet will not take the heat of the rod, sharply reducing its temperature).
Disadvantages of copper sting:
- Softness and low heat resistance - the rod quickly oxidizes at high temperature, loses its functionality. You have to clean it with a file or sandpaper. The result is that the sting turns into a short one over time and needs to be replaced.
To keep the surface of the copper rod in working condition, it is covered with a thin layer of solder, protecting it from oxidation.
Blade with nickel-plated (removable tips) are equipped with EPSN soldering irons and with a ceramic heater.
The advantages of a coated sting:
- Do not burn, do not need descaling and sharpening.
Disadvantages of coated sting:
- Higher price;
- They are afraid of overheating.
The body of the ceramic tip is made of ceramic, and its tip is made of metal (copper, coated with nickel).
The advantages of ceramic sting:
- Good thermal conductivity and heat capacity;
- Corrosion resistance;
- No need for regular cleaning.
Disadvantages of ceramic sting:
- High price;
- The fragility of the body.
Sting shape
Depending on the work performed using a tip of a certain shape. Not all models of soldering irons are designed to use interchangeable tips, the replacement of the tip in such an instrument takes a long time. When purchasing a soldering iron, it is necessary to clarify whether it is designed to work with interchangeable tips.
Basic, most popular forms of sting:
- Wedge (screwdriver);
- Core with beveled edge;
- Cone;
- Needle.
Handle material
It is preferable to stop the choice on the model with a handle of a material with low thermal conductivity:
- Tree;
- Ebonite;
- Carbolite;
- Textolite.
Cheap models have a non-heat resistant plastic handle that heats up quickly and can even melt. If there is a choice, it is better to give preference to a wooden handle - wood conducts heat worse than all available structural materials.
Which soldering iron to choose
Recommendations on the choice of tools, depending on the work performed:
1. To work with three-dimensional parts, for example, to solder a cable, you need a tool with a copper tip and a power of at least 40 watts.
2. For desoldering resistors, diodes use ceramic soldering irons with a power of 3-10 W with a nickel tip.
3. For regular work with microcircuits, the requirements for the soldering iron are as follows: power not more than 20 W, thin tips in the configuration, the presence of a temperature controller, preferably a ceramic heater.
4. For use in everyday life, when it is necessary to solder the wire, repair the household appliance - EPSN with a power of 25-40 W and with a copper sting.
5. For soldering wires in car service or private garage, a powerful EPSN soldering iron (up to 100 W) with a copper tip.
How much are electric soldering irons

The price of a soldering iron depends on the brand of the instrument, its technical characteristics, the type of heater, the presence of the thermostat, the number and type of tips in the configuration.
Indicative prices are as follows:
1. EPSN with a copper sting, power 40 W - from 80 to 600 rubles.
2. Ceramic with a nichrome heater, with a durable sting (nickel), power 30-40 W - from 300 to 600 rubles.
3. With a film-ceramic heater, with a durable sting, the power of 50 W - from 2500 thousand rubles. up to 5200 thousand rubles.
4. Pulse soldering iron, power 70 W - from 360 to 700 rubles.
5. USB and wireless soldering irons, power up to 10 W - from 300 to 1300 rubles.
It will be interesting to friends too